Configuring STid readers that use the SSCP protocol to prevent relay attacks
2024-05-09Last updated
Prevent relay attacks on supported STid readers by enabling the system to detect delays in the RF communication exchanges between cards and readers, and reject access requests from the cards that take too long to communicate.
Before you begin
- This procedure only applies to STid readers that are using the SSCP or SSCP V2 protocol and running firmware v21 or later.
- Enable DESFire EV2 secure messaging.
What you should know
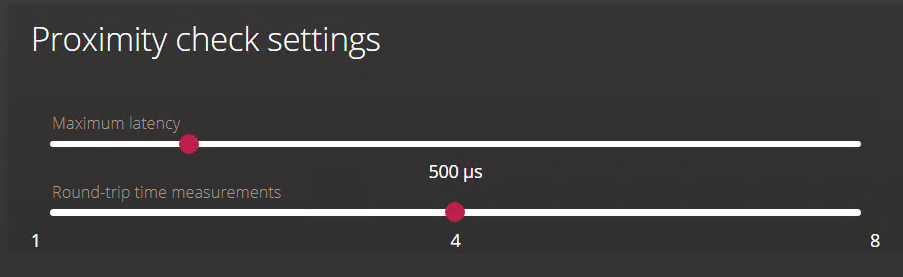
Enabling a proximity check on STid readers ensures that only access requests from cards that fall within a configured time threshold are granted.
Procedure
Example
The proximity check results in one of
the following:
- If the time calculated for each of the four exchanges falls within the Maximum latency, the card succeeds the proximity check. The Synergis Cloud Link unit proceeds to grant or deny access based on the access rights of the card, and the door unlocks or remains locked accordingly.
- If at least one of the exchanges takes longer than the Maximum
latency, the card fails the proximity check. The
Synergis Cloud Link unit does not proceed to make an access
decision, and the door remains locked.Note:No Access denied event is generated when a proximity check fails.